Posts Tagged ‘Polaris’
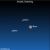
Earthsky Tonight—August 3, Dipper points to Polaris,
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org The two outer stars in the bowl of the Big Dipper – Dubhe and Merak – always point to Polaris, the North Star. To find this Dipper at this time of year, look toward the northwest in the evening. Once you have found it – after locating Polaris – look more carefully at the second star from the end of the Big Dipper’s handle. If your sky is dark enough, and your eyesight is good, you will see that this star, Mizar, has a ... Full Story
Earthsky Tonight—July 4, Draco the Dragon on July

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org At nightfall tonight, the starlit Eyes of Draco the Dragon peer down upon you from almost overhead. Their names are Eltanin and Rastaban. If the sun, Eltanin and Rastaban all were located the same distance from us, it’s thought that Eltanin would shine 600 times more brightly than our sun and that Rastaban would shine 950 times more brightly. Though Rastaban is actually the more luminous of these two stars, Eltanin appears ... Full Story
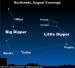
Earthsky Tonight—July 1: Big Dipper points to

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org Today our star-hopping adventure begins at the Big Dipper in the constellation Ursa Major. Draw a line through the Big Dipper’s pointer stars – Duhbe and Merak – to locate Polaris the North Star. Polaris isn’t the brightest star in the sky, as is commonly supposed. It is only the 50th brightest or so. Still, Polaris is bright enough to be seen with relative ease on a dark, clear night. This star is famous not for its ... Full Story
Earthsky Tonight—June 3: See Draco the Dragon and a
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org If you have a dark sky, you will be able to pick the constellationDraco the Dragon winding around the North Star, Polaris. First, find the Big Dipper high in the north on June evenings. The two outer stars in the Dipper’s bowl point to Polaris, the North Star, which marks the end of the Little Dipper’s handle. The Little Dipper is relatively faint. If you can find both Dippers, then your sky is probably pretty dark. In ... Full Story
Earthsky Tonight—June 2: Little Dipper, Clipped

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org The Little Dipper is an asterism – a star pattern that is not a constellation. The Little Dipper really belongs to the constellation Ursa Minor the Little Bear. Richard Hinkley Allen in his book STAR NAMES Their Lore and Meaning claims the Greek constellation Ursa Minor was never mentioned in the literary works of Homer (9th century B.C.) or Hesiod (8th century B.C.). That is probably because this constellation was not around at ... Full Story
Earthsky Tonight—June 1: Big Dipper high in north on

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org Here is the legendary Big Dipper, now high in the north during the evening hours. It is one of the most familiar star patterns in the sky because its shape really resembles a dipper. Less familiar – and tougher to find – is the Little Dipper. Here is how you can find it. First, locate the Big Dipper in the northern sky during the evening hours. Notice that the Big Dipper has two parts: a bowl and a handle. See the two outer ... Full Story
Earthsky Tonight—May 24: Bright star near moon is

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org The waxing gibbous moon glides past the star Spica in the constellation Virgo this evening. It passes relatively close to Spica for a day or two each month that Spica is visible in our night sky. It does the same with other bright stars such as Regulus in the constellation Leo, Antares in the constellation Scorpius and Aldebaran in the constellation Taurus. Have you ever heard of the moon near Polaris the North Star? If someone ... Full Story
Earthsky Tonight — April 9: Star-hop to Canes
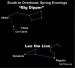
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org We show a larger section of sky than we normally do on this chart. We’re looking directly overhead at about 10:00 p.m., viewing the sky from the comfort of a reclining lawn chair, with our feet pointing southward. The constellation Leo the Lion stands high in the southern sky, while the upside-down Big Dipper is high in the north. Tonight, we star-hop to the constellation Canes Venatici the Hunting Dogs by using the Big Dipper ... Full Story
Earthsky Tonight—April 7, 2010: Kochab and Pherkad

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org If you draw an imaginary line between the two outer stars in the bowl of the Big Dipper – and extend that line northward on the sky’s dome – you’ll come to Polaris, the North Star. Polaris marks the end of the handle of the Little Dipper, which is fainter and looks less like a dipper than the Big Dipper. Polaris is special because Earth’s northern axis nearly points to it. Polaris is less than a degree away from true ... Full Story
Earthsky Tonight — April 6, 2010: Use Big Dipper to
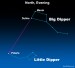
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org Here is the view northward on April evenings. Now the Big Dipper is high in the north. Notice the two outer stars in the bowl of the Big Dipper. These two stars – called Duhbe and Merak – always point to Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is special because it always stays in the same spot in the northern sky. It is the star around which the entire northern sky appears to turn. That is because Polaris is located more or less ... Full Story