Posts Tagged ‘Rigel’
Sky Tonight—April 19, Moon and Scorpion rise after

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org Like clockwork, the constellations rise and set 4 minutes earlier with each passing day. Four minutes doesn’t sound like much, but it adds up after a while. For instance, the stars rise and set one half-hour earlier with each passing week, or 2 hours earlier with each passing month. That is six hours difference after one 3-month season. Tonight, the red supergiant star Antares rises in the southeast around ... Full Story
Sky Tonight—February 14, Blue-white Rigel is at the

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org Jupiter is the dazzling object in the west after sunset The three sparkling blue-white stars of Orion’s Belt are easy to spot, even on this moonlit night. As viewed from this hemisphere, this compact line of stars can be found in the south to southeast sky at nightfall. Look in the southern sky at evening and the southwest sky later tonight. Chances are the pattern you will pick out will be Orion! You may ... Full Story
Sky Tonight—February 13, Moon points the way to

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org Tonight’s waxing gibbous moon resides inside the Winter Circle – an incredibly large star configuration made of six brilliant winter stars. Be sure to notice the variety in the colors of these stars. The Winter Circle – sometimes called the Winter Hexagon – is not one of the 88 recognized constellations. Rather, it is an asterism – a pattern of stars that is easy to recognize. Our sky chart cannot ... Full Story
Sky Tonight—February 10, Somber red Betelgeuse

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org At nightfall and early evening, people at mid-northern latitudes see the famous Belt of Orion – three stars in a short, straight row – about halfway between the southern horizon and straight overhead. Later at night, you will find Orion in the southwest. Above Orion’s Belt, you will find one of the sky’s most famous stars, ruddy-hued Betelgeuse. Kids especially like Betelgeuse, because its name sounds ... Full Story
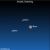
Sky Tonight—January 23, Eridanus-a winding river of
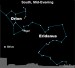
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org Bright star in southwest on January evenings? It’s the planet Jupiter Here is a constellation for you if you have access to a very dark sky: Eridanus the River. You will not see this one from the city, or even the suburbs. Eridanus the River begins near the star Rigel in the constellation Orion the Hunter – and wells up in a great loop before ambling back down toward the southern horizon. Rigel: Orion’s ... Full Story
Sky Tonight—January 21, Identify the Winter Circle

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org Tonight’s chart covers a wider area of sky than what we typically show. It is in answer to a reader in Nashville, who wrote, I have heard mention of the Winter Circle of Stars. Could you list the stars in this circle? You will find these stars at this time of year by looking east-southeast at early to mid evening. Again, this is a large pattern and covers a wide area of sky, but as always, it is easiest to start ... Full Story
Sky Tonight—January 20, Orion the Hunter easy to
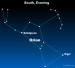
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org The constellation Orion the Hunter is probably the easiest to pick out of all the constellations in the winter sky. It is identifiable by Orion’s Belt, three medium-bright stars in a short, straight row at the mid-section of the Hunter. See these stars? They are easy to spot on the sky’s dome. As seen from mid-northern latitudes, you will find Orion in the southeast at nightfall and shining high in the ... Full Story
EarthSky Tonight, December 15: Bellatrix—Orion’s
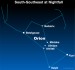
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org The third-brightest star in Orion, Bellatrix, is often overlooked. Yet, Bellatrix is such a wonderful star. According to Richard Hinckley Allen’s classic book Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning, the Latin name Bellatrix means Female Warrior, which some find odd since the original Arabic title translates as the Conqueror. But women understand. Bellatrix represents Orion’s left shoulder. Although it appears ... Full Story
December 14, Focus on stars Betelgeuse and Rigel in
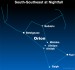
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org Orion the Hunter is one of the most prominent constellations in all the heavens. You cannot fail to spot Orion’s Belt – three medium-bright stars in a short, straight row – if you look eastward in the evening. The magnificent Orion Nebula, or M42, is a fuzzy patch in Orion’s Sword. Most constellations have only one bright star, but Orion has two: Rigel and Betelgeuse. Rigel is Orion’s left foot. A ... Full Story
EarthSky Tonight—December 6, Winter Circle up by

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org You will have to stay up until 9 or 10 p.m. tonight to see the exceptionally brilliant and huge Winter Circle filling up the eastern portion of sky. This famous sky pattern is not a constellation. It is an asterism: a noticeable pattern on the sky’s dome. In this case, the pattern is made of the brightest stars of winter, in many different constellations. From a dark sky, you will see the Milky Way’s hazy band ... Full Story