Posts Tagged ‘Betelgeuse’
Sky Tonight—April 19, Moon and Scorpion rise after

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org Like clockwork, the constellations rise and set 4 minutes earlier with each passing day. Four minutes doesn’t sound like much, but it adds up after a while. For instance, the stars rise and set one half-hour earlier with each passing week, or 2 hours earlier with each passing month. That is six hours difference after one 3-month season. Tonight, the red supergiant star Antares rises in the southeast around ... Full Story
Sky Tonight—March 12, Moon between Capella and

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org The first quarter moon will be shining between two brilliant stars tonight. Capella, the brightest star in the constellation Auriga, will be beaming north of the moon, while Betelgeuse, the star marking the right shoulder in the constellation Orion, will be shining south of the moon. From mid-northern latitudes in Europe and Asia, you will see the moon farther west (right), and closer to the star Aldebaran, than ... Full Story
Sky Tonight—February 14, Blue-white Rigel is at the

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org Jupiter is the dazzling object in the west after sunset The three sparkling blue-white stars of Orion’s Belt are easy to spot, even on this moonlit night. As viewed from this hemisphere, this compact line of stars can be found in the south to southeast sky at nightfall. Look in the southern sky at evening and the southwest sky later tonight. Chances are the pattern you will pick out will be Orion! You may ... Full Story
Sky Tonight—February 10, Somber red Betelgeuse

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org At nightfall and early evening, people at mid-northern latitudes see the famous Belt of Orion – three stars in a short, straight row – about halfway between the southern horizon and straight overhead. Later at night, you will find Orion in the southwest. Above Orion’s Belt, you will find one of the sky’s most famous stars, ruddy-hued Betelgeuse. Kids especially like Betelgeuse, because its name sounds ... Full Story
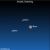
Sky Tonight—January 20, Orion the Hunter easy to
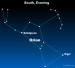
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org The constellation Orion the Hunter is probably the easiest to pick out of all the constellations in the winter sky. It is identifiable by Orion’s Belt, three medium-bright stars in a short, straight row at the mid-section of the Hunter. See these stars? They are easy to spot on the sky’s dome. As seen from mid-northern latitudes, you will find Orion in the southeast at nightfall and shining high in the ... Full Story
Sky Tonight—January 6, Use bright stars to find
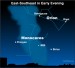
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org You will need a very dark sky to see the constellation Monoceros the Unicorn on these cold January nights. How can you find the Unicorn? Focus in on the bright stars Betelgeuse, Sirius and Procyon. They make a triangle, sometimes called the Winter Triangle. Within this triangle of stars, hidden in between the many bright and glittering stars and constellations visible at this time of year, there is a ... Full Story
EarthSky Tonight—December 9, Find Orion the Hunter
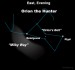
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org You can find one of winter’s most famous constellations – Orion the Hunter – plus see the Milky Way tonight. Orion is bright and can be seen from inside smaller cities. For the Milky Way, you will need a dark sky! On these evenings in early to mid-December, the constellation Orion rises over your eastern horizon 2 to 3 hours after sunset. Orion swings south to his highest point around midnight, then sets ... Full Story
EarthSky Tonight—Nov 27, Orion the Hunter rises in
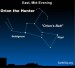
Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science Visit EarthSky at www.EarthSky.org Orion the Mighty Hunter – perhaps the easiest to identify of all constellations – rises at mid-evening in late November and early December. Depending on where you live, Orion will climb over your eastern horizon by around 8 to 9 p.m. tonight. Orion appears to be lying on his side when he first ascends into our eastern sky. Orion’s Belt of three moderately-bright stars juts more or less straight upward from ... Full Story
Earthsky Tonight—April 29, Moon and Scorpion rise as

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org Like clockwork, the constellations rise and set 4 minutes earlier with each passing day. Four minutes doesn’t sound like much, but it adds up after a while. For instance, the stars rise and set one-half hour earlier with each passing week, or 2 hours earlier with each passing month. That is 6 hours difference after one 3-month season. In late April, the red supergiant star Antares rises in the southeast around 11:00 p.m. local ... Full Story
Earthsky Tonight — April 28, Orion descends in the

Courtesy of EarthSky A Clear Voice for Science www.EarthSky.org At this time of year, the famous constellation Orion is descending in the southwest to west in the hours after sunset. Orion is noticeable for its bright stars and its distinctive pattern on the sky’s dome. Look for three stars in a short, straight row. Then look for Betelgeuse and Rigel, Orion’s brightest stars. If you didn’t come to know it this winter, check it out now. It is one of the most distinctive of all star ... Full Story